- Types of planning in principles of management textbook
- 4 Functions of Management Process: Planning, Organizing, Leading, Controlling
- Types of planning in principles of management essay
- Types of planning in principles of management quizlet
It is best expressed at the beginning of a project in terms of key and measurable criteria upon which the relative success or failure of the project may be judged. For example, some generally used success criteria include: Meeting key project objectives such as the business objectives of the sponsoring organization, owner or user Eliciting satisfaction with the project management process, i. e., the deliverable is complete, up to standard, is on time and within budget Reflecting general acceptance and satisfaction with the project's deliverable on the part of the project's customer and the majority of the project's community at some time in the future. Conclusion Simplilearn offers multiple Project Management training courses and learning paths that can help aspiring project managers get the education they need—not only to pass exams like the PMP certification but also real-world knowledge useful for any project management career. Want a taste of Simplilearn project management training?
Types of planning in principles of management textbook
By " participated development ", we mean a process through which stakeholders influence and share control over development initiatives and decisions that affect them. see ⇒ The participatory approach Proactive participation among stakeholders, be it within a community or an organisation, enables the exchange of ideas and opinions, information sharing and interpersonal rapport that is grounded in mutual respect and shared responsibilities, and working together towards common and mutual objective Cooperation. Getting the participation of the poor requires strengthening the organizational and financial capacities of the poor so that they can act for themselves. The constructive dialogue between civil society and local authorities is an essential prerequisite for a sustained and participated development. Participation is a process through which stakeholders influence and share control over development initiatives and the decisions and resources which affect them. Participation in political science is an umbrella term including different means for the public to directly participate in political, economical or management decisions.
Project management is a composite activity with multiple dimensions. Depending on the type and class of the project, this management activity can be very complex. In a nutshell, project management is the discipline of planning, organizing, securing, managing, leading, and controlling resources to achieve specific goals. What Is Project Management About? The very basics of project management are as follows: a project is a temporary endeavor with a defined beginning and end (usually time-constrained, and often constrained by funding or deliverables) that an organization takes to meet unique goals and objectives, typically to bring about beneficial change or add value. The primary challenge of project management is to achieve all of the project goals and objectives while honoring the pre-defined constraints. The primary constraints are scope, time, quality, and budget. The secondary—and more ambitious—challenge is to optimize the allocation of necessary inputs and integrate them to meet pre-defined objectives.
Thus, there will be better coordination in the organisation.
4 Functions of Management Process: Planning, Organizing, Leading, Controlling
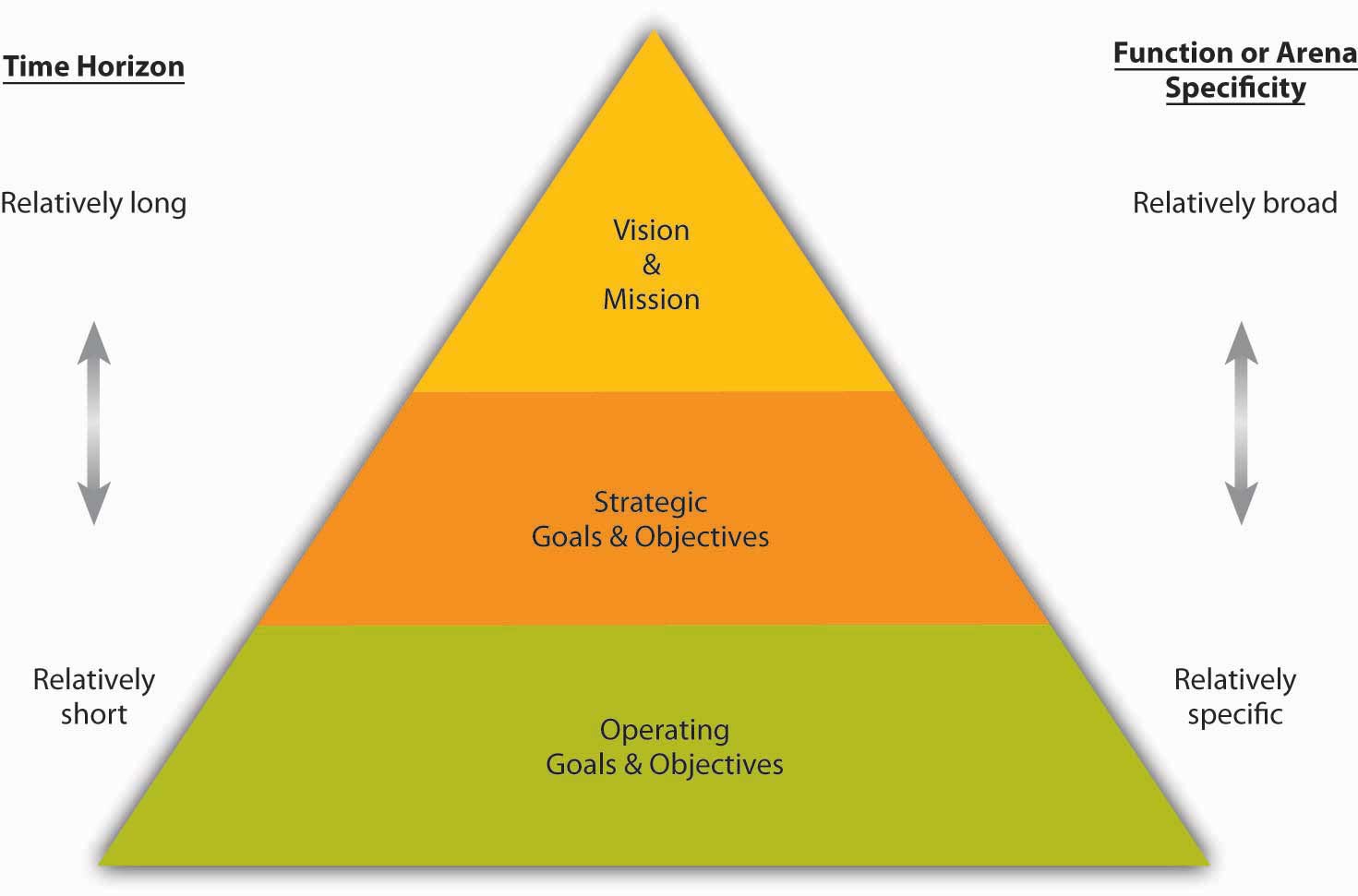
Creating the operational plan is the responsibility of low-level managers and supervisors. Operational plans can be either single use, or ongoing, as described below: 1. Single Use Plans These plans are created for events/activities with a single occurrence. This can be a one-time sales program, a marketing campaign, a recruitment drive, etc. Single use plans tend to be highly specific. 2. Ongoing Plans These plans can be used in multiple settings on an ongoing basis. Ongoing plans can be of different types, such as: Policy: A policy is a general document that dictates how managers should approach a problem. It influences decision making at the micro level. Specific plans on hiring employees, terminating contractors, etc. are examples of policies. Rule: Rules are specific regulations according to which an organization functions. The rules are meant to be hard coded and should be enforced stringently. "No smoking within premises", or "Employees must report by 9 a. m. ", are two examples of rules.
Make it fun" These aren't fragments from a motivational speech, but 's values. Like Fab, each organization has its own values. These values will guide managers and influence the kind of employees you hire. There is no template to follow when jotting down the values. You can write a 1, 000 page essay, or something as simple as Google's "Don't be Evil" – it's all up to you. As you can see, there are really no rules to writing the perfect strategic plan. This is an open-ended, living document that grows with the organization. You can write whatever you want in it, as long as it dictates the future of your organization. For inspiration, just search for the value/mission/vision statement of your favorite companies on Google. Or, consider taking this course on business planning for average people. II. Tactical Plan The tactical plan describes the tactics the organization plans to use to achieve the ambitions outlined in the strategic plan. It is a short range (i. e. with a scope of less than one year), low-level document that breaks down the broader mission statements into smaller, actionable chunks.
Types of planning in principles of management essay
Tactical Plans Tactical plans describe the tactics that the managers plan to adopt to achieve the objectives set in the strategic plan. Tactical plans span a short time frame (usually less than 3 years) and are usually developed by middle level managers. It details specific means or action plans to implement the strategic plan by units within each division. Tactical plans entail detailing resource and work allocation among the subunits within each division. Operational Plans Operational plans are short-term (less than a year) plans developed to create specific action steps that support the strategic and tactical plans. They are usually developed by the manager to fulfill his or her job responsibilities. They are developed by supervisors, team leaders, and facilitators to support tactical plans. They govern the day-to-day operations of an organization. Operational plans can be − Standing plans − Drawn to cover issues that managers face repeatedly, e. g. policies, procedures, rules. Ongoing plans − Prepared for single or exceptional situations or problems and are normally discarded or replaced after one use, e. programs, projects, and budgets.
In addition, the importance of planning is that it plays a vital role to the survival and growth of an organization as it ensures accuracy, economy, and operational efficiency. Planning also has many different hats for it plays a positive role in the business environment, helps make uniform decisions, sets performance standards, and helps the organization solve problems and challenges that are present every day. Without planning, an organization can expect inefficiency, confusion, disorder, and wasting valuable resources in both human and material. Planning is one of the most important function of management because of the following factors: Makes the objectives clear and specific: planning clearly specifies the objectives and the policies or activities to be performed to achieve these objective in other words what is to be done and how it is to be done are clarified in planning. Off setting the uncertainty and change: planning is necessary to look ahead towards future and to take decisions regard facing the expected changes/requirement of the future.

Types of planning in principles of management quizlet
- Catalogo office depot 2019 pdf free
- Types of planning in principles of management ppt
- Importance of Planning in Management - MBA Knowledge Base
- Detailing Types of Plans
- Types of planning in principles of management worksheet
- Types of planning in principles of management class
- Sustainable Business/Booklets - Wikibooks, open books for an open world
- Types of planning in principles of management course
- Oficio de trabajo format adobe
- Proyecto de inversion de un restaurante vegetariano
Marketing budgets Building your credibility Your competitive advantages Finance [ edit] Three key documents The profit and loss forecast Cashflow budget Steps in preparing a cash budget Special points The balance sheet Break-even calculation Your business idea: a quick test The Four Fives Rule New Zealand business structure, tax and compliance [ edit] What business structure should you choose?
E. g. before coming of summer session producers started production for the products to be used in summer. Plans facilitate decision-making: to achieve the objective predetermined under planning, business has to take various decisions by considering the available resources. If job may be completed by using various alternatives (e. manually or by machines) and the best alternative is decided by the management, which is more helpful in achieving the objective. Provides basis of control: under controlling actual performance is compared with the planed performance (target/objective). So planning is the base of controlling process. Leads to economy and efficiency: planning clarifies the work and its method of doing. Resultantly it reduces confusion and wastage of resources in the form of thinking at the time of doing. So efficiency of the worker will risen which will further result economy in production. Facilitates integration: under planning proper directions as per plane are provided to the subordinates.
Sun, 28 Feb 2021 12:39:03 +0000